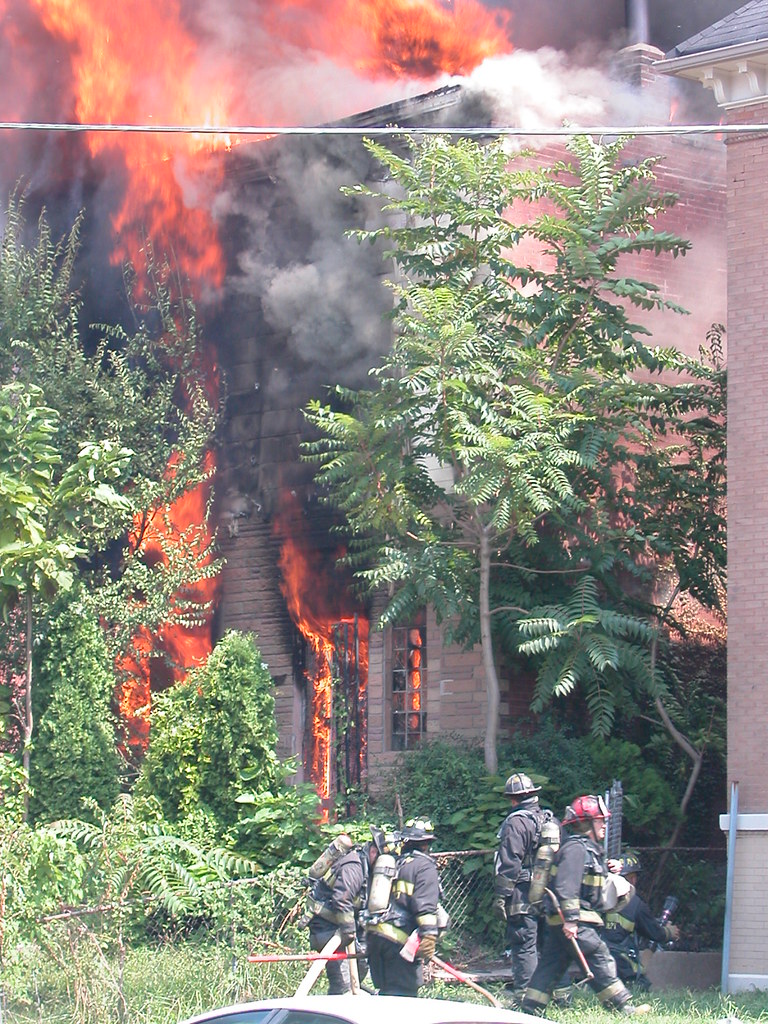
 A sweltering, humid afternoon yesterday broke what had been a string of some of the most pleasant St. Louis summer days in recent years. In the Fountain Park neighborhood, the dog day brought more than just unpleasant weather. At around 12:40 p.m., a fire broke out at the abandoned home at 1124 Bayard Avenue. The blaze roared through a modest two-story home that has experiences fire twice before, according to a neighbor.
A sweltering, humid afternoon yesterday broke what had been a string of some of the most pleasant St. Louis summer days in recent years. In the Fountain Park neighborhood, the dog day brought more than just unpleasant weather. At around 12:40 p.m., a fire broke out at the abandoned home at 1124 Bayard Avenue. The blaze roared through a modest two-story home that has experiences fire twice before, according to a neighbor. Neighbors who had been hanging out indoors in search of air conditioning came outside to watch a mid-day spectacle that is unfortunately a common occurrence in much of north St. Louis. Firefighters were quick to respond, and had the fire under control quickly. The firefighters surely earned the respect of the assembled crowd on Labor Day afternoon.
Neighbors who had been hanging out indoors in search of air conditioning came outside to watch a mid-day spectacle that is unfortunately a common occurrence in much of north St. Louis. Firefighters were quick to respond, and had the fire under control quickly. The firefighters surely earned the respect of the assembled crowd on Labor Day afternoon.The house was not one of the stunning homes that line Fountain park proper, nor was it the nearby "castle" building. (The sight of dark smoke coming from near that structure made me shiver.) The brick home has acquired permastone on the first floor and flimsy siding above. Still, it had been a solid residence until going vacant two years ago. Its altered facade still made up part of a street scape wall that joins others to form the architectural context of life in Fountain Park. The house had a supporting role to the fancier buildings, but its loss will make the drama a little less full.
The neighborhood atmosphere yesterday was a far cry of the vision of John Lay, the Virginia farmer who platted 158 acres of his land just west of the city limits in 1857. Dubbing the subdivision "Aubert Place," Lay envisioned a fashionable middle-class enclave centered on an elegant park, like those he had seen in London. Early advertisements suggest that Aubert Place was a country retreat, and certainly the character of this area supported that assertion. Development was slow, even though half of the lots sold at auction in 1857. One reason for slow growth was the distance for public transit, which would not come for nearly another twenty years.
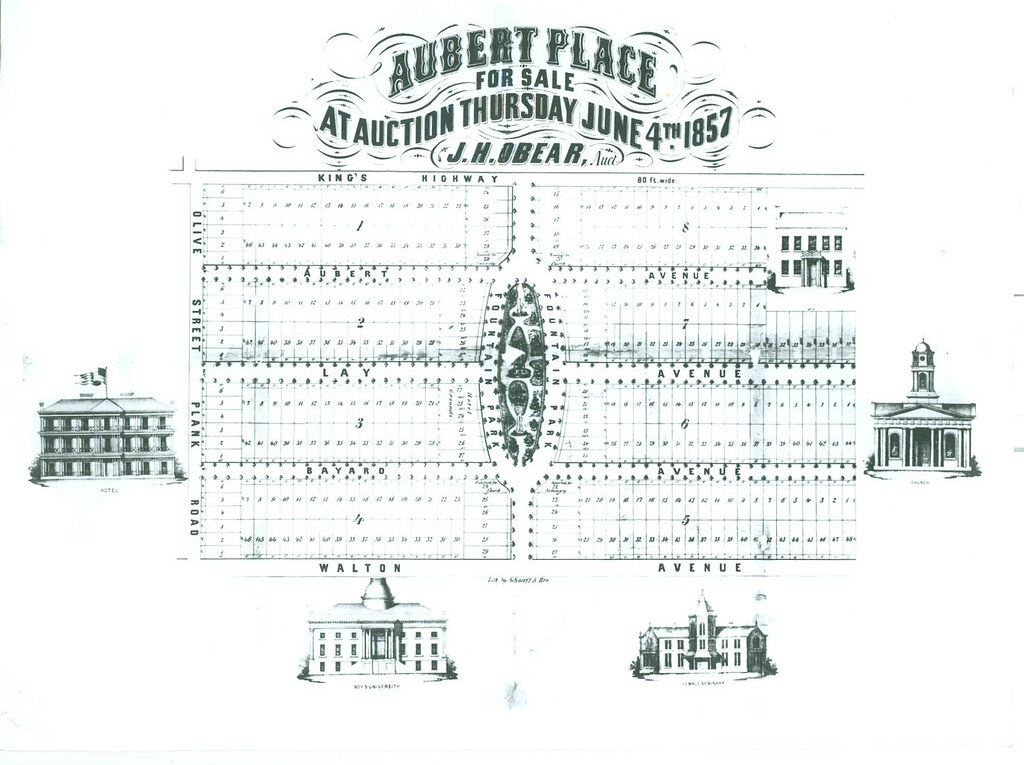 Most early homes here were frame, and only forty had been built by 1883. Still, annexation into the city in 1876 encouraged growth, as did the continued westward growth of the city. Streetcars came down Delmar to the south and Easton to the north, with a line also running straight down Euclid through the heart of the development. Development of the Central West End in the early 1890s coincided with the city's investment in the park in 1889. The city took the undeveloped central feature of Aubert Place and built amenities, including the fountain that would lead to the gradual name change of the neighborhood. Lay's charming suburb had been missing the elegance of a well-planned park. With lots reserved for single-family homes and a required twenty-foot set-back, Aubert Place was destined to be genteel. Building was rapid between 1892 and 1897, when two brothers named Davis built many homes. A second boom covers the years of 1903 through 1925, when unrestricted blocks around the original subdivision were developed with two-flats and other multi-family properties. Now known as Fountain Park, the neighborhood thrived with middle-class residents.
Most early homes here were frame, and only forty had been built by 1883. Still, annexation into the city in 1876 encouraged growth, as did the continued westward growth of the city. Streetcars came down Delmar to the south and Easton to the north, with a line also running straight down Euclid through the heart of the development. Development of the Central West End in the early 1890s coincided with the city's investment in the park in 1889. The city took the undeveloped central feature of Aubert Place and built amenities, including the fountain that would lead to the gradual name change of the neighborhood. Lay's charming suburb had been missing the elegance of a well-planned park. With lots reserved for single-family homes and a required twenty-foot set-back, Aubert Place was destined to be genteel. Building was rapid between 1892 and 1897, when two brothers named Davis built many homes. A second boom covers the years of 1903 through 1925, when unrestricted blocks around the original subdivision were developed with two-flats and other multi-family properties. Now known as Fountain Park, the neighborhood thrived with middle-class residents.In the 1940s, Africa-Americans began piercing the housing restrictions in Fountain Park, at the time when many whites were leaving for more fashionable addresses west and north. A renewal took place, and the community remained strong for several decades until signs of decay crept in. To this day, there is amazing dichotomy in Fountain Park. Many blocks are very well-kept and retain their original beauty, while other blocks are marked by vacant lots, boarded buildings and vestiges of vice. Not surprising, the original Aubert Place is stronger than the outer tier of multi-family buildings. The posh Victorian middle-class suburb is now a problem-ridden 21st-century American urban neighborhood. That is to say, that for every day like yesterday, it has another good day. And for every beautiful home on Fountain, there's a house like 1124 Bayard.
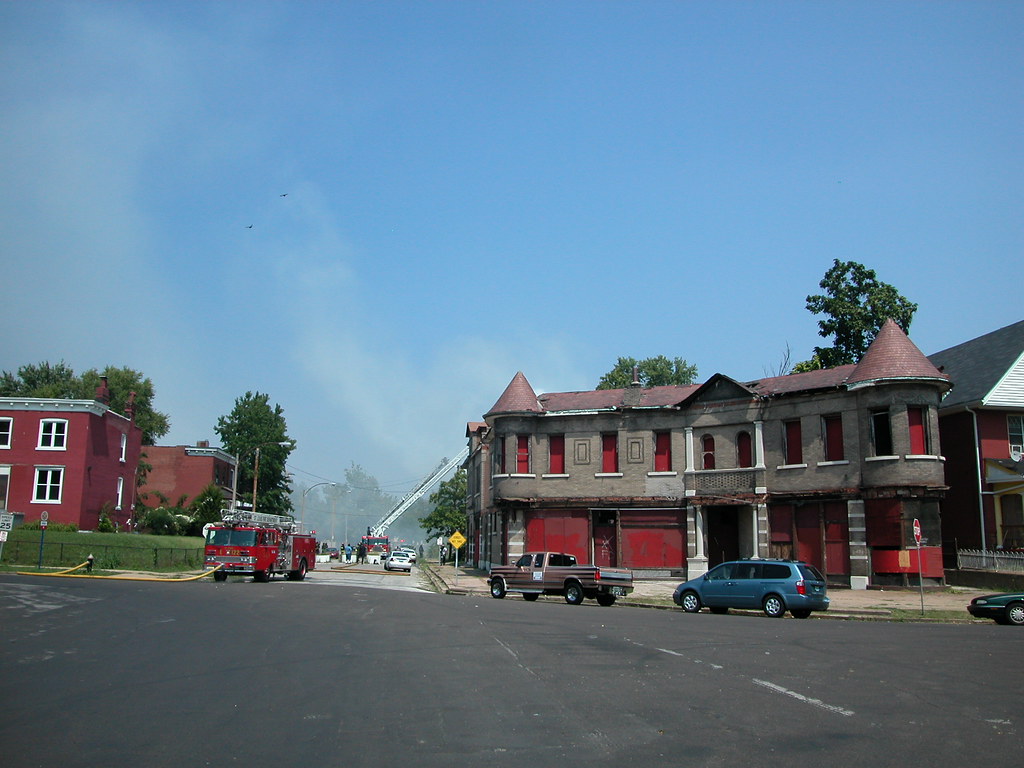

More coverage:





1 comment:
Ha! That commercial building in the foreground is the same one that Toby Wiess caught the "rehabbers" stealing the ornamental iron from the facade. Except at the time, she bought their "oh, yeah, we're rehabbing the building" schtick. Fool me once...Though I'm betting she was a little suspicious of their activities.
Post a Comment